Download

Downloading Pose Analysis
With just an iPhone or iPad, you can easily track 3D poses and analyze the data on the spot.
Utilize it for research in fields such as medicine, engineering, and sports.
Pose AnalysisAbout
Pose Analysis tracks the subject in real-time 3D using the iPhone/iPad camera.
The inference model used for this estimation is a domestically developed model by Digital Standard Co., which has been utilized in multiple medical research papers.
Additionally, this app provides features that allow users to apply filters to the joint coordinate data obtained through the inference, calculate joint angles, and easily display the data in graphs, enabling quick on-the-spot analysis of the captured data.
With the web dashboard, users can manage and visualize the data taken by members.
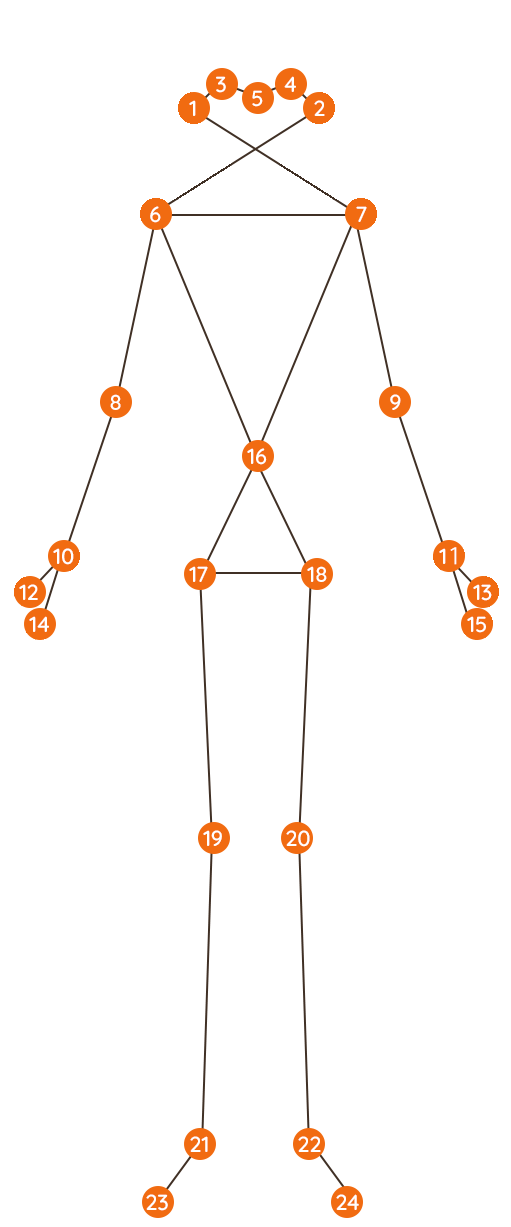
Detection Points
- Right ear
- Left ear
- Right eye
- Left eye
- Nose
- Right shoulder
- Left shoulder
- Right elbow
- Left elbow
- Right wrist
- Left wrist
- Base of right thumb
- Base of left thumb
- Base of right middle finger
- Base of left middle finger
- Abdomen
- Right hip
- Left hip
- Right knee
- Left knee
- Right ankle
- Left ankle
- Right toe
- Left toe
Camera
Support for the both of cameras

- Front camera
- Back camera
Frame rates
You can select from the following frame rates.

- 30fps
- 60fps
Paper resultsPaper results
- 01
- Evaluation of Upper and Lower Limb Movement Variability during Gait in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus and Parkinson's Disease Using the Smartphone Application TDPT-GT for Motion Capture
Evaluation of Upper and Lower Limb Movement Variability during Gait in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus and Parkinson's Disease Using the Smartphone Application TDPT-GT for Motion Capture
This paper presents a study that evaluates the variability in upper and lower limb movements during gait in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) and Parkinson's disease (PD) using the smartphone application "TDPT-GT" for motion capture. In the study, 23 patients with iNPH, 23 patients with PD, and 2 healthy controls were analyzed while walking in a circle with a diameter of 1 meter. The movement of various body parts was recorded at 30Hz, and the variability in these movements was analyzed. The analysis showed a significant reduction in variability across all body positions in both the iNPH and PD patient groups compared to the healthy controls. Notably, iNPH patients demonstrated a greater reduction in upper and lower limb variability than PD patients. These results suggest that reduced movement variability during gait may contribute to gait and balance impairments in iNPH and PD patients. This study demonstrates that detailed evaluation of gait characteristics in iNPH and PD patients is possible through motion capture using a smartphone application, potentially providing valuable insights for future diagnosis and rehabilitation strategies.
- 02
- Identification of Pathological Gait Using Artificial Intelligence: Analysis of Markerless Motion Capture Gait Data Acquired by the iOS Application (TDPT-GT)
Identification of Pathological Gait Using Artificial Intelligence: Analysis of Markerless Motion Capture Gait Data Acquired by the iOS Application (TDPT-GT)
This study focuses on the evaluation of gait, which is critical in neurological diagnosis, addressing the challenge of capturing whole-body movement. The objective is to obtain convenient recordings using an iPhone and establish an algorithm based on deep learning. From May 2021 to November 2022, gait data were collected from 114 patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH), Parkinson's disease (PD), and other neuromuscular diseases, as well as 160 healthy volunteers, at Yamagata University Hospital, Shiga University, and Takahata Town. Using the iPhone application TDPT-GT, participants were recorded walking along a circular path with a diameter of about 1 meter. From the 2D images captured by the iPhone camera, 3D heatmaps were estimated, and the relative coordinates of 27 body points along three axes at 30 frames per second (fps) were generated. A model was built using deep learning with Light GBM (Light Gradient Boosting Machine) to distinguish between pathological and normal gait, achieving an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.719. The feature importance scores indicated that the y-coordinate of the right hip had the highest significance, followed by the depth of the pelvis, the depth of the right knee, and the x-coordinate of the head center. In conclusion, pathological gait captured by an iPhone can be identified using artificial intelligence. This study offers a new approach for gait analysis in the diagnosis and treatment of neurological diseases.
- 03
- Quantitative Gait Feature Evaluation on the Body Axis Projection Plane Derived from 3D Coordinates Estimated by a Deep Learning Smartphone Application
Quantitative Gait Feature Evaluation on the Body Axis Projection Plane Derived from 3D Coordinates Estimated by a Deep Learning Smartphone Application
This paper discusses a method for quantitatively evaluating pathological gait based on 3D coordinates estimated using a deep learning model. In the study, 15 healthy volunteers demonstrated four gait patterns: normal walking, shuffling gait, short stride, and wide stride. Next, the gait of 47 patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) and 92 healthy elderly individuals from the Takahata cohort was evaluated using the TDPT-GT application. Two-dimensional relative coordinates were calculated from the 3D coordinates, and indicators related to pathological gait were comprehensively explored from these 2D relative coordinates. The results showed that a hip joint angle range of less than 30 degrees was a candidate indicator for shuffling gait, a knee joint angle range of less than 45 degrees for short stride, and an outer leg shift of 0.1 or more for wide stride. This study demonstrated that the TDPT-GT application enables easy evaluation of various pathological gait patterns without requiring a large-scale 3D motion analysis system.
Function Introduction機能紹介

01
Cloud Storage and Data Export
Export the detected positions of each joint
during pose estimation to a CSV file.
By making an in-app purchase, you can save the measurement data within the app and upload it to the cloud.

02
Calculation of Joint Angles
Specify the target CSV file and calculate
the angles of each joint frame by frame.

03
Visualization of Estimation Results
iPad: While replaying videos and stick figures from pose estimation,
you can check the positions and angles of each joint on graphs.
iPhone: Display the positions and angles of each joint
on graphs within the app to observe motion changes.
Additionally, you can view the following filtered data
applied to the exported raw data:
- Kalman Filter
- Low-pass Filter

04
Team Management and Web Dashboard
Create multiple members within a team
and share measurement tickets for use.
Additionally, by logging into the dedicated web dashboard,
you can view a list of data measured and uploaded by team members
and visualize it on graphs.
PricePrice
- Realtime Three D Pose Tracking
- Unlimited (Check the estimation results with a stick figure while recording with the camera)
But you need to pay for saving the result data in local and upload to cloud. - Save the estimation results in local
- Unlimited
- Upload data to the web platform
- 100 yen per 10 times
- Web Dashboard
- Unlimited
- Team Management
- Unlimited
Notes
- Only one subject
It is not possible to estimate the poses of two people simultaneously. - Supported devices
Models released after iPhone 11. Android is not supported.
Video playback and stick figure player functions are only available on iPad.
Introducing the Related AppTDPT
TDPT -Three D Pose Tracker-
https://digital-standard.com/tdpt_lp/
- Developed by Digital Standard Co.
- Control VRM models in real-time using the TDPT engine
- Send motion data using the VMC protocol
- Live streaming
- Motion data output (VMD/BVH formats) etc
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
Before contacting us...
Please check the “FAQ - Frequently Asked Questions”
page.
Contact
Inquiries
For inquiries regarding Pose Analysis,
please contact us at the email address below.